The L/C payment method—short for Letter of Credit—is a trusted financial tool used in international trade to ensure secure transactions between buyers and sellers. It acts as a guarantee from the buyer’s bank that payment will be made to the seller once specific conditions are met. This method is especially valuable in cross-border deals where trust, legal systems, and logistics vary widely.
What Is the L/C Payment Method?

A Letter of Credit is a written commitment from a buyer’s bank (the issuing bank) to pay the seller (the beneficiary) a specified amount, provided the seller presents documents that comply with the terms of the credit. These documents typically confirm that the goods have been shipped as agreed.
The L/C payment method is governed by international rules, most notably the Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP), issued by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). These rules standardize procedures and reduce ambiguity across borders.
How the L/C Payment Method Works?
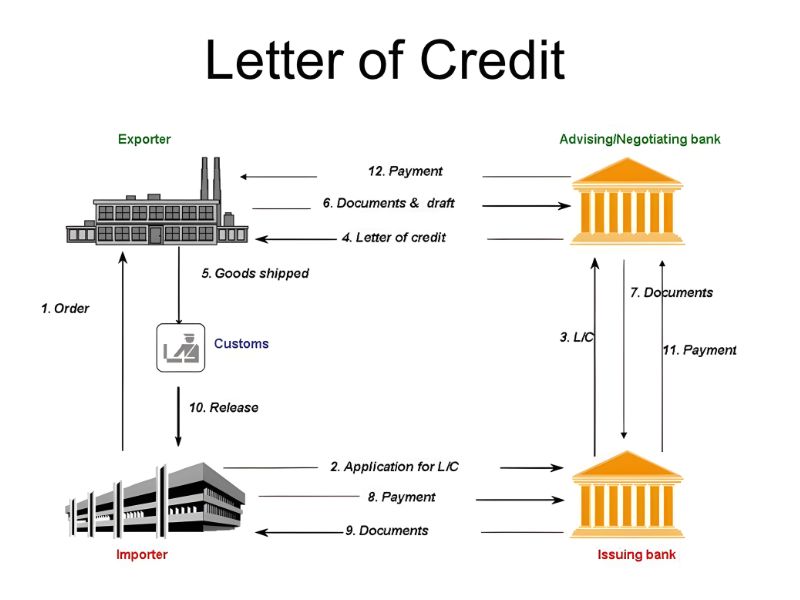
The process of using an L/C payment method involves several key steps:
Contract and Application: The buyer and seller agree on trade terms and sign a commercial contract. The buyer then requests their bank to issue a Letter of Credit in favor of the seller.
Issuance and Notification: The issuing bank creates the L/C and sends it to a bank in the seller’s country—called the notifying or advising bank—which informs the seller and provides the original document.
Seller Review: The seller reviews the L/C to ensure it matches the contract. If discrepancies exist, they may request amendments.
Shipment and Documentation: The seller ships the goods and prepares all required documents, such as the bill of lading, invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin.
Document Presentation: The seller submits the documents to the notifying bank.
Verification and Payment: The notifying bank forwards the documents to the issuing bank. If compliant, payment is made to the seller, and the buyer receives the documents to claim the goods.
Types of L/C Payment method
There are several types of Letters of Credit, each suited to different trade scenarios:
Revocable L/C: Can be changed or canceled by the buyer without prior notice to the seller. Rarely used due to high risk for the seller.
Irrevocable L/C: Cannot be altered without agreement from all parties. This is the most common and secure type.
Confirmed L/C: A second bank (usually in the seller’s country) adds its guarantee to the L/C, offering extra security.
Sight L/C: Payment is made immediately upon document verification.
Usance (Deferred) L/C: Payment is made after a specified period post-document verification.
Transferable L/C: Allows the seller to transfer part or all of the credit to another party, often used in intermediary trade.
Roles of the Issuing and Notifying Banks
Banks play a central role in the L/C payment method:
Issuing Bank: Located in the buyer’s country, this bank issues the L/C and guarantees payment if terms are met.
Notifying/Advising Bank: Located in the seller’s country, this bank informs the seller of the L/C and may assist in document handling.
Confirming Bank (if applicable): Adds its own guarantee to the L/C, ensuring payment even if the issuing bank defaults.
These banks ensure that the transaction is secure, compliant, and executed according to international standards.
Benefits and Risks of L/C payment
Benefits
- For Sellers: Guaranteed payment from a reputable bank, even if the buyer defaults.
- For Buyers: Payment is only made after the seller proves shipment via compliant documents.
- For Both Parties: Reduces risk in cross-border transactions and builds trust.
Risks
- Document Discrepancies: Minor errors can lead to delayed or denied payment.
- Bank Charges: Fees can be significant, especially for confirmed or transferable L/Cs.
- Complexity: Requires careful attention to detail and understanding of trade documentation.
FAQ About L/C Payment

Is L/C Payment Safe?
Yes, the L/C payment method is considered one of the safest options in international trade. It ensures that the seller receives payment only after fulfilling the agreed terms, and the buyer only pays when shipment is verified.
What Are the Rules for L/C Payment?
L/C transactions are governed by the UCP 600 rules issued by the ICC. These rules define the responsibilities of banks, the format of documents, and the procedures for handling discrepancies.
Who Is Eligible for L/C?
Any business engaged in international trade can use the L/C payment method. However, banks may require credit checks or collateral from buyers before issuing an L/C. Sellers should also have the capacity to produce and present compliant documents.
How Much Do Banks Charge for L/C?
Fees vary depending on the type and complexity of the L/C. Common charges include:
- Issuance Fee: Paid by the buyer to the issuing bank
- Advising Fee: Paid by the seller to the notifying bank
- Confirmation Fee: Additional cost if a confirming bank is involved
- Document Handling Fee: Charged for processing and verifying documents
These fees can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the transaction size and risk level.
Final Thoughts
The L/C payment method is a cornerstone of secure international trade. It offers protection, structure, and trust for both buyers and sellers navigating complex global transactions. Whether you’re shipping woven fabric from Vietnam or importing electronics from Europe, using an L/C can help ensure that your business gets paid—and gets what it paid for. By understanding how the L/C payment method works, its types, the roles of banks, and its benefits and risks, traders can make informed decisions and reduce uncertainty in cross-border commerce.

