FSSC 22000 Certification, or Food Safety System Certification, is a vital framework in the food industry aimed at managing food safety effectively. This internationally recognized standard enhances food safety and builds trust among consumers and stakeholders. In an era where ensuring safety and quality is paramount, FSSC 22000 certification provides a structured approach for organizations to achieve these critical goals. In this article, we will explore what FSSC 22000 is, its key components, benefits, comparisons to other certifications, steps to achieve certification, and common challenges along with strategies to overcome them.
What Is FSSC 22000 Certification?

FSSC 22000 combines the ISO 22000 standard with additional sector-specific requirements, creating a comprehensive food safety management system. It is applicable to all organizations in the food supply chain, including producers, manufacturers, and distributors, as well as those handling packaging materials such as woven bags. This certification provides a robust framework for ensuring that food products are safe for consumption, addressing risks throughout the entire food supply chain.
Key Components of FSSC 22000 Certification
The key components of FSSC 22000 consist of several crucial elements. First, ISO 22000 serves as the foundational standard that outlines the requirements for a food safety management system. This system emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach, focusing on the entire food supply chain.
Additionally, prerequisite programs (PRPs) are essential for maintaining hygiene and safety in food production processes. These programs cover critical areas, including facility design, pest control, and employee training, ensuring that basic food safety measures are in place. FSSC 22000 also includes sector-specific requirements tailored to various food industries, ensuring the certification remains relevant across different sectors. Finally, continuous improvement is a core principle of FSSC 22000, promoting regular audits and updates to foster a culture of safety and quality within organizations.
Benefits of FSSC 22000 Certification
Achieving FSSC 22000 certification offers a multitude of benefits for organizations. One of the primary advantages is enhanced food safety, as the certification provides a structured approach to managing food safety risks, resulting in safer food products. In addition, certification increases consumer trust; it signals to customers that your organization is committed to maintaining high food safety standards, thereby boosting loyalty.
Moreover, many retailers and buyers require FSSC 22000 certification as a prerequisite for doing business, creating opportunities for market access. This certification also contributes to improved operational efficiency, streamlining processes and reducing waste. Furthermore, FSSC 22000 helps organizations comply with local and international food safety regulations, minimizing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
FSSC 22000 Certification vs Other Certifications

When comparing FSSC 22000 to other food safety certifications, its comprehensive nature becomes evident. For example, HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) is crucial for food safety but often adopts a reactive approach. In contrast, FSSC 22000 promotes a proactive, systematic methodology for managing food safety.
Similarly, ISO 9001 focuses on quality management systems, while FSSC 22000 specifically addresses food safety, making it more relevant for stakeholders in the food industry. BRCGS (British Retail Consortium Global Standards) is widely recognized, particularly in Europe, but FSSC 22000’s alignment with ISO standards offers greater adaptability for global operations. Lastly, SQF (Safe Quality Food) is another comprehensive certification, yet FSSC 22000’s integration with ISO standards may appeal to organizations seeking a standardized approach.
Steps to Get FSSC 22000 Certified
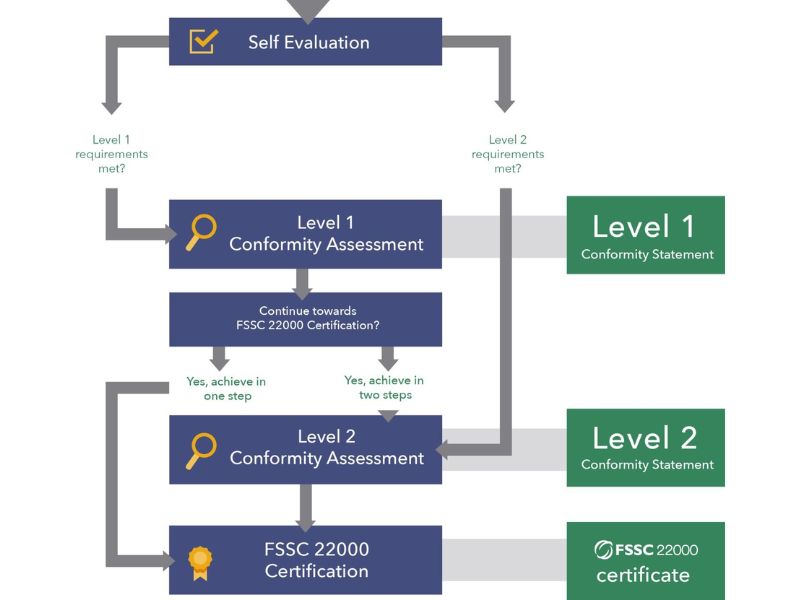
The process of obtaining FSSC 22000 certification involves several key steps. First, organizations should conduct a gap analysis to assess areas where existing practices may fall short of FSSC 22000 requirements. This initial assessment is critical for identifying necessary improvements.
Next, training is essential; organizations should provide employees with necessary training on food safety management principles and practices. Following this, organizations must develop and implement the required food safety management system, integrating ISO 22000 and PRPs into their operations.
After implementation, conducting internal audits ensures that the system functions as intended and that all requirements are being met. Once internal preparations are complete, organizations can engage a recognized certification body to perform an external audit to assess compliance with FSSC 22000 standards. Finally, after achieving certification, organizations should focus on continuous improvement through regular monitoring and updates to maintain compliance and enhance food safety.
Common Challenges & How to Overcome Them
Pursuing FSSC 22000 certification can present several challenges. One common hurdle is a lack of awareness among employees regarding the importance of food safety management. To address this, organizations should provide regular training sessions and workshops to raise awareness about FSSC 22000 and its benefits.
Resource constraints can also be an issue, especially for smaller organizations. A phased approach can help, allowing for incremental improvements without overstretching available resources. Additionally, resistance to change may occur as employees adjust to new processes and systems. Engaging staff early in the certification process and encouraging feedback can foster a culture of ownership and acceptance.
Another challenge is the documentation overload that comes with certification requirements. Organizations can streamline documentation processes by utilizing digital tools that simplify record-keeping and ensure easy access to essential information. Lastly, maintaining compliance after certification requires ongoing effort. Regular audits, both internal and external, can help organizations stay compliant and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
FSSC 22000 certification is a critical step for organizations aiming to enhance food safety and build trust with consumers. By understanding its components, benefits, and the certification process, businesses can position themselves as leaders in food safety. Whether you are a producer, manufacturer, or distributor, embracing FSSC 22000 will not only improve food safety management but also provide a competitive edge in the increasingly demanding food industry.

